Understanding Dermatitis: Impacts and Treatments
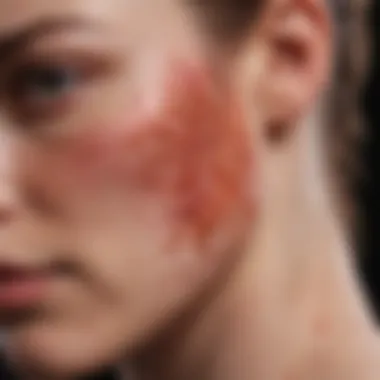

Intro
Dermatitis is an umbrella term that encompasses various inflammatory skin conditions, each with its unique characteristics and implications. Understanding this complex field is essential, as the effects of dermatitis extend far beyond the skin. This article aims to provide a comprehensive examination of dermatitis, focusing on its side effects, causes, and potential treatments.
The importance of this topic cannot be overstated. Individuals dealing with dermatitis often experience physical discomfort and emotional distress, affecting their overall well-being. By exploring the multifaceted nature of dermatitis, we hope to shed light on how it impacts individuals and society at large. Through detailed discussions on symptoms, treatments, and preventive strategies, we aim to empower readers with knowledge to manage their condition better.
As we move through this article, expect to engage with various research insights and expert opinions, allowing for a rounded grasp of dermatitis. The exploration will guide you through symptoms, treatment options, lifestyle adjustments, and preventive measures crucial for those affected by skin disorders.
Overview of Dermatitis
Dermatitis is a significant and multifaceted condition that deserves attention due to its widespread prevalence and diverse impact on those afflicted. Understanding dermatitis involves recognizing its many forms and the commonalities they share, particularly in terms of skin inflammation. This comprehension leads to a better approach in treating and managing the condition.
Dermatitis can vary in presentation and severity, and it often interplays with various physical and psychological aspects of health. One cannot overlook how this condition affects individuals daily, leading not only to physical discomfort but also to emotional and social consequences. By exploring dermatitis comprehensively, we can grasp the extensive ramifications it has on the quality of life for people.
Definition of Dermatitis
Dermatitis refers to the inflammation of the skin characterized by redness, swelling, and discomfort. It encompasses various types of skin conditions, each denoted by specific causes, symptoms, and management strategies. The term itself broadly indicates a range of inflammatory skin conditions which can manifest in different ways but generally involve a similar underlying inflammatory process.
Types of Dermatitis
Understanding the different types of dermatitis is crucial for proper diagnosis and treatment. Each type exhibits unique symptoms and triggers, necessitating targeted approaches for effective management.
Atopic Dermatitis
Atopic dermatitis, often known as eczema, is a chronic condition marked by itchy, inflamed skin. The key characteristic of atopic dermatitis is its tendency to flare up periodically, which can lead to cycles of discomfort and relief. This type of dermatitis is prevalent among children but can occur at any age. Atopic dermatitis is often associated with other allergic conditions, such as asthma and hay fever, making its understanding beneficial for those in the medical field. It’s important to recognize the psychosocial implications, as the visible nature of this condition can affect self-esteem.
Contact Dermatitis
Contact dermatitis arises when the skin reacts to substances it touches. This type is divided into allergic contact dermatitis and irritant contact dermatitis. The primary characteristic of contact dermatitis is the localized nature of the reaction, often resulting in red, itchy patches or blisters. Identifying the offending agents can lead to effective prevention and management, emphasizing the need for thorough patient education regarding skin care and exposure avoidance. The unique feature of contact dermatitis is that it can often be prevented by recognizing and avoiding triggers, contributing to the focus on preventive measures within this article.
Seborrheic Dermatitis
Seborrheic dermatitis typically affects oil-rich areas of the body, such as the scalp and face. This rare condition is often marked by flaky and red patches that can be unsightly and sometimes itchy. A key characteristic of seborrheic dermatitis is its association with an overgrowth of a natural yeast that lives on the skin. This understanding highlights the necessity for targeted antifungal treatments and lifestyle adjustments to manage symptoms effectively.
Stasis Dermatitis
Stasis dermatitis occurs when there is insufficient blood flow to the skin, often associated with vascular disease. The hallmark of this condition is swelling in the legs and the subsequent development of itchy, irritated skin. Stasis dermatitis emphasizes the relationship between systemic health and skin conditions. Understanding it allows healthcare providers to approach the treatment not only of the skin but also of the underlying circulatory problems, thus enhancing overall patient care.
Common Causes of Dermatitis
Understanding the common causes of dermatitis is crucial as it forms the foundation for effective management and treatment of the condition. Identifying specific triggers can lead to targeted solutions, helping individuals mitigate their symptoms more efficiently. The discussion focuses on genetic factors, environmental triggers, and lifestyle considerations, all of which play significant roles in the onset and exacerbation of dermatitis. By recognizing these causes, sufferers can make informed choices which enhance their quality of life.
Genetic Factors
Genetic factors significantly influence the likelihood of developing dermatitis. Individuals with a family history of skin conditions may be more susceptible to developing various types of dermatitis, particularly atopic dermatitis. Genetic markers can affect skin barrier function, immune response, and overall skin health. Understanding one's genetic predispositions can lead to earlier diagnosis and tailored treatment strategies.
Environmental Triggers
Environmental triggers encompass external factors that can aggravate or provoke dermatitis. These include allergens, irritants and climate conditions.
Allergens
Allergens are substances that can provoke an immune response, leading to inflammation in the skin. Common allergens associated with dermatitis include pollen, pet dander, and certain foods. This type of reaction is critical to address since its elimination can lead to improvement of symptoms. The key characteristic of allergens is their ability to instigate immediate hypersensitivity in susceptible individuals. Identifying and avoiding these triggers is often a beneficial approach in managing dermatitis effectively.
Irritants
Irritants comprise chemicals or substances that, upon contact with the skin, cause inflammation. Common irritants include soaps, detergents, and certain fabrics. Unlike allergens, irritants can provoke dermatitis without a prior sensitization process. Their pervasive presence in everyday life highlights the need for awareness. Understanding the nature of irritants is essential as it allows individuals to change their daily habits and routines to foster skin health.
Climate Conditions
Climate conditions can also influence the development and worsening of dermatitis. Factors such as humidity, temperature extremes, and exposure to the sun can exacerbate symptoms. The critical aspect of climate-related triggers is their variability, as some individuals might react adversely to certain environments. Understanding how climate impacts skin health can guide sufferers in taking preventive actions during unfavorable conditions.
Lifestyle Factors
Lifestyle factors also play a pivotal role in dermatitis.


Stress
Stress is a known exacerbator of various skin conditions, including dermatitis. Psychological stress can affect the immune system, leading to increased inflammation and flare-ups. This connection underscores the importance of stress management techniques. Recognizing stress as a contributory factor empowers individuals to seek solutions that address both psychological health and skin wellness.
Dietary Influences
Dietary influences can also contribute to the onset and severity of dermatitis. Some studies suggest that certain diets lacking in essential nutrients may compromise skin integrity. On the other hand, adopting a balanced diet rich in antioxidants, vitamins, and minerals may support skin health and mitigate symptoms. Understanding one's dietary habits becomes imperative in forming a holistic approach to managing dermatitis.
Skin Care Practices
Skin care practices directly influence the skin's health and resilience. Using appropriate moisturizers and avoiding products with harsh chemicals can help maintain the skin barrier. The key characteristic of beneficial skin care practices lies in their ability to enhance skin hydration and reduce irritation. Implementing suitable practices not only aids in managing dermatitis but also promotes overall skin health.
A comprehensive understanding of what causes dermatitis generates better prevention and treatment strategies.
Physical Side Effects
Understanding the physical side effects of dermatitis is crucial in grasping the overall impact of the condition. Physical symptoms can significantly affect the quality of life for individuals who experience dermatitis. By recognizing and addressing these symptoms, patients and healthcare providers can work toward effective management strategies. The most common physical side effects include skin symptoms, secondary infections, and scarring or hyperpigmentation.
Skin Symptoms
Redness and Inflammation
Redness and inflammation are often among the first indicators of dermatitis. These symptoms result from an immune response to irritants or allergens, leading to increased blood flow to the affected areas. The key characteristic of redness is its visibility, which makes it easily recognizable. This immediate feedback is a beneficial component of discussing dermatitis, as it alerts individuals to potential flare-ups. However, it can also be a distressing feature, contributing to social anxiety or emotional distress due to the visible nature of the condition.
Additionally, inflammation can lead to skin swelling, making the affected areas throb or feel warm to the touch. While it serves as a useful marker for worsening conditions, such inflammation often brings discomfort, requiring careful management techniques.
Dryness and Cracking
Dryness and cracking are significant concerns for dermatitis sufferers. This symptom arises due to a compromised skin barrier that fails to retain moisture. The key characteristic here is the texture of the skin, which often appears parched and can lead to pain when cracking occurs. This aspect is central to this article since it illustrates the physical discomfort associated with dermatitis. Cracked skin may be more prone to infections, adding a layer of complexity to treatment and care.
The unique feature of dryness and cracking lies in the cyclic nature of skin hydration; excessive dryness can prompt further use of topical treatments, yet over-application can lead to irritation. Awareness of this balance is crucial for effective skin care management.
Itching and Discomfort
Itching and discomfort are often described as the most frustrating aspects of dermatitis. The sensation of itchiness can lead to scratching, which may aggravate skin conditions further. This symptom contributes to sleep disruptions and affects daily activities, making it a critical point in understanding the overall experience of dermatitis.
The key characteristic of itching is its psychosomatic ties. It can be exacerbated by stress, anxiety, or environmental conditions. This makes addressing the symptom imperative for a holistic approach. Notably, the discomfort caused by itching and other pain remains one of the top reasons individuals seek medical intervention regarding dermatitis.
Secondary Infections
Secondary infections can arise when the integrity of the skin barrier is compromised. Open wounds from scratching or cracked skin provide an entry point for bacteria or other pathogens. These infections can exacerbate the original dermatitis, leading to increased inflammation and redness.
Additionally, dealing with infections complicates the treatment plan. Antibacterial or antifungal medications may become necessary, and these treatments may add another layer of complexity to managing one's skin condition. Therefore, it's important to understand the risks associated with secondary infections as part of a comprehensive approach to dermatitis management.
Scarring and Hyperpigmentation
Scarring and hyperpigmentation are often long-term consequences of dermatitis, particularly when it is not effectively managed. Persistent inflammation can lead to tissue damage, resulting in scars. Hyperpigmentation occurs when the skin produces excess melanin in response to inflammation or irritation. It is critical to address these concerns because they can impact both physical appearance and emotional well-being.
The unique feature of scarring and hyperpigmentation is their lasting nature. Unlike the temporary symptoms of redness or itching, scars and discoloration can remain long after the initial condition has resolved. This permanence can have psychological effects, contributing to feelings of embarrassment or low self-esteem.
Understanding these physical side effects serves as the foundation for effective treatment and lifestyle adjustments in managing dermatitis. By recognizing the various symptoms and their implications, individuals can make informed decisions geared towards improved skin health.
Psychological Impact of Dermatitis
The psychological impact of dermatitis is significant but often overlooked in medical discussions. This impact ranges from emotional distress to broader considerations of overall quality of life. Understanding this aspect is critical because it helps to highlight the interconnected nature of physical conditions and mental health. Patients with dermatitis do not merely suffer from visible skin symptoms; they often face a range of psychological challenges that can exacerbate their condition. Exploring these themes can lead to better treatment approaches and enhance individual coping strategies.
Emotional Distress
Anxiety
Anxiety is prevalent among those dealing with dermatitis. It manifests as a persistent feeling of worry or fear that can interfere with daily activities. The visible nature of skin issues often makes individuals self-conscious, increasing anxiety levels. One important characteristic of anxiety in this context is its cyclic effect: as symptoms worsen, anxiety increases, which can further aggravate the skin condition. Recognizing this connection is crucial for a comprehensive understanding of dermatitis.
Anxiety can be a common response to the unpredictability of flare-ups. Patients may also fear judgment from others based on their appearance. This makes anxiety a relevant focus in this article. Managing anxiety can lead to improved skin outcomes, thus highlighting the beneficial approach of including mental health considerations in treatment plans.
Depression
Depression can develop due to the ongoing struggle with dermatitis. Its symptoms, such as sadness and a lack of interest in previously enjoyable activities, can leave individuals feeling isolated. The unique feature of depression in dermatological conditions is its link to chronic illness; patients might feel trapped in a cycle where physical symptoms contribute to negative moods.


By addressing feelings of despair and hopelessness, better strategies can be implemented. Depression impacts treatment adherence too. Understanding its role in the lives of patients allows healthcare providers to offer more supportive care, which is vital for overall well-being.
Social Withdrawal
Social withdrawal often accompanies emotional distress in dermatitis patients. This behavior involves avoiding social interactions due to embarrassment or discomfort about one's appearance. The characteristic here is a reduction in engagement with friends, family, and communities, which can worsen feelings of isolation and depression over time.
Social withdrawal is a relevant choice for this article because it highlights how mental health affects lifestyle choices. While it may provide temporary relief from anxiety, it ultimately intensifies feelings of loneliness. In addressing this issue, fostering social connections can help patients feel understood and supported.
Impact on Quality of Life
The overall quality of life can be significantly diminished by dermatitis. Factors such as physical discomfort, sleep disturbances, and emotional struggles intertwine, affecting daily functioning. Many patients report a lower sense of well-being, affecting their job performance and personal relationships.
Addressing both physical and psychological elements is essential for holistic care. Improved treatment approaches should integrate psychological support to enhance life satisfaction. Understanding how dermatitis affects various aspects of life is crucial for developing effective interventions that go beyond treating the skin.
Treatment Overview
The process of treating dermatitis is multifaceted, reflecting the condition's complexity. Treatment options vary widely, and selecting the right one is crucial for effective management. Understanding the various medical and alternative treatments available can greatly enhance a patient’s quality of life. Each option comes with specific benefits and considerations that merit careful examination.
Medical Treatments
Topical Corticosteroids
Topical corticosteroids are among the most common treatments for dermatitis. They work by reducing inflammation, which helps alleviate symptoms like redness and itching. This is vital because inflammation is a significant contributor to discomfort and further skin irritation. A key characteristic of topical corticosteroids is their potency; they come in various strengths, allowing customization based on the severity of the condition.
Some individuals may prefer topical corticosteroids due to their quick effects and ease of application. However, prolonged use can lead to skin thinning and other side effects. It’s essential to use these medications under medical supervision to balance benefits and risks effectively.
Immunomodulators
Immunomodulators offer another avenue for dermatitis treatment, particularly for moderate to severe cases. They work by altering the immune response underlying inflammation. This class of medication is beneficial for individuals who do not respond well to corticosteroids or those who experience unacceptable side effects from them.
One significant feature of immunomodulators is their ability to provide long-term control of symptoms without the adverse effects associated with steroids. Still, these medications require a careful management plan, as not all patients will experience similar results. Continuous monitoring is advised to assess efficacy and side effects.
Phototherapy
Phototherapy involves exposing the skin to specific wavelengths of light. This treatment can significantly reduce inflammation and is particularly considered for individuals with chronic conditions. The key characteristic of phototherapy is its ability to reach the deeper layers of skin without the systemic side effects of oral medications.
While phototherapy can be very effective, it requires multiple sessions over weeks or months to achieve desired results. There is also a time commitment, as sessions can be frequent. Patients may also have concerns regarding long-term exposure to UV light, necessitating a discussion with their healthcare provider about safety and effectiveness.
Alternative and Complementary Approaches
Herbal Remedies
Herbal remedies are increasingly explored as complementary treatments for dermatitis. These remedies often focus on reducing inflammation and soothing the skin. A notable characteristic is that many herbal products are considered less harsh than conventional medications.
The appeal of herbal remedies lies in their natural origins, with various options available, such as chamomile and aloe vera. However, users must be cautious, as not all herbal products are thoroughly researched. It is advisable to consult healthcare providers before starting any new regimen to ensure safety and efficacy.
Acupuncture
Acupuncture is another alternative approach some individuals find beneficial. This ancient practice involves inserting thin needles into specific body points to balance energy flow. The key characteristic of acupuncture is its holistic nature, aiming to treat both physical and emotional symptoms of dermatitis.
While some evidence suggests acupuncture may help reduce symptoms, results can be variable. It is essential to seek a qualified practitioner, as the expertise of the acupuncturist significantly influences outcomes. Discussions about this treatment should include potential benefits and realistic expectations.
Mindfulness Practices
Mindfulness practices are becoming more recognized in the realm of skincare. These techniques, including meditation and breathing exercises, focus on reducing stress. Stress is often a trigger for dermatitis flare-ups; hence, managing stress can be an effective strategy.
The unique feature of mindfulness is its simplicity; it often requires no special products or extensive time commitments. Regular practice can enhance a person’s mental well-being, potentially reducing symptoms of dermatitis. However, it is not a standalone treatment and should be integrated into a broader management plan for best results.
Understanding the various treatments available for dermatitis is crucial. Each option presents distinct benefits and drawbacks, requiring careful consideration and consultation with healthcare professionals.
Preventive Measures
Understanding how to prevent dermatitis is essential for those affected and can reduce the likelihood of flare-ups. Preventive measures focus on managing the condition before it escalates, especially for individuals with a history of dermatitis. By developing effective skincare routines and adopting lifestyle adjustments, individuals can mitigate the chances of exacerbating their symptoms. This section emphasizes proactive steps that can significantly enhance skin health and overall quality of life.
Skincare Routines


A consistent skincare routine plays a pivotal role in managing dermatitis. Gentle products designed for sensitive skin can help maintain skin hydration and barrier function. It is advisable to:
- Use fragrance-free and hypoallergenic cleansers.
- Moisturize immediately after bathing to lock in moisture.
- Avoid products containing alcohol, which can worsen dryness.
These actions help reduce irritation and promote skin healing. Regular exfoliation can also be beneficial; however, it should be done cautiously to avoid further skin damage. Choosing products wisely is important to prevent irritation and keep skin healthy.
Lifestyle Adjustments
Making specific lifestyle adjustments can significantly influence the severity of dermatitis symptoms.
Stress Management
Stress is a notable trigger for dermatitis flare-ups. It can worsen existing conditions and provoke new episodes. Thus, managing stress effectively is vital. Techniques like meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises are popular choices. These practices help individuals diminish anxiety and promote relaxation. By integrating stress management into daily life, one can lower the chances of experiencing flare-ups.
Healthy Diet
Nutrition also contributes to skin health. A well-balanced diet rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants can support the body's immune system and skin function. Focusing on:
- Fruits and vegetables, which provide essential nutrients.
- Omega-3 fatty acids, known to reduce inflammation.
- Hydration, crucial for overall skin moisture.
The unique feature of a healthy diet is its ability to improve skin resilience over time. However, individual responses to specific foods can vary. It is essential for individuals to monitor their diet and identify any potential food triggers associated with their dermatitis.
Avoiding Known Triggers
Identifying and avoiding known triggers is a fundamental strategy for managing dermatitis. Triggers can vary widely among individuals and can include:
- Certain fabrics like wool or synthetic materials.
- Environmental factors such as pollen or dust.
- Harsh soaps or cleaning products.
Understanding personal triggers can help minimize exposure and potential flare-ups. Keeping a diary to track symptoms in relation to exposure can be beneficial. By systematically eliminating triggers from one’s environment, affected individuals can greatly reduce their risk of dermatitis aggravation.
"Prevention is always better than cure; understanding what triggers dermatitis is key to effective management."
By focusing on preventive measures such as a careful skincare routine, lifestyle adjustments, and knowledge of triggers, individuals can aspire to achieve better skin health and improved overall well-being.
Future Directions in Dermatitis Research
Research in the field of dermatitis is continually evolving. Understanding the recent trends and future directions is vital to improve management and treatment options for individuals affected by this condition. Areas like genetic advancements and new therapeutic strategies have significant potential to reshape how dermatitis is perceived and treated. These directions not only promise more personalized healthcare but also enhance the hope for long-term solutions.
Advancements in Genetics
Genetics plays a crucial role in skin disorders, including various types of dermatitis. Recent studies focus on identifying the genes associated with dermatitis susceptibility. The exploration of genetic predisposition is essential because it helps clarify why some individuals develop the condition while others do not.
Understanding these genetic factors can offer insights into the underlying mechanisms of dermatitis. For instance, research has uncovered specific gene mutations that increase the likelihood of developing atopic dermatitis.
This information is valuable for two primary reasons:
- Tailored Treatments: Genetic insights can guide personalized treatment approaches, reducing the trial-and-error associated with current therapies.
- Preventive Strategies: Identifying genetic markers may allow for early intervention, possibly preventing the onset of dermatitis in those genetically predisposed.
New Therapeutic Strategies
The treatment landscape for dermatitis is rapidly changing, driven by innovation and research. One of the most promising directions is the development of biologics. These are targeted therapies that can specifically address the inflammatory pathways involved in dermatitis, offering potential relief for patients who do not respond to traditional treatments.
Advancements in drug delivery systems are also significant. For example, transdermal delivery devices are under exploration. These can enhance the effectiveness of medications, ensuring they penetrate the skin more efficiently.
Moreover, ongoing clinical trials are investigating new formulations and combinations of existing therapies that could provide better results with fewer side effects. This illustrates an exciting time in dermatitis research as scientists continually seek to maximize treatment outcomes.
"The future of dermatitis treatment lies in understanding individual needs and tailoring interventions accordingly."
Engagement with community-based research initiatives, alongside traditional laboratory studies, is crucial to verify findings in real-world settings. Collaborations between academia and industry can support the emergence of innovative solutions and improved patient care.
Epilogue
The conclusion serves as a critical component in understanding dermatitis and its multifaceted effects. Synthesizing the information presented throughout the article is essential to reinforce the idea that dermatitis is not merely a superficial concern, but a condition that can permeate both physical and psychological well-being.
In reviewing the side effects of dermatitis, this article has highlighted the importance of recognizing early signs, such as redness, inflammation, and itching. Addressing these physical symptoms can prevent potential complications, such as secondary infections and long-term skin damage, including scarring and hyperpigmentation.
Moreover, the psychological impact must not be overlooked. Emotional distress stemming from visible skin problems can lead to social withdrawal, anxiety, and even depression. This underscores the necessity for a holistic approach in managing dermatis, which includes not only physical treatments but also psychological support.
Key Points
- Recognizing the symptoms early can facilitate timely interventions.
- A comprehensive approach should incorporate both medical treatments and lifestyle adjustments.
- Education about triggers and preventive measures is crucial in managing this condition effectively.
The exploration of future directions for dermatitis research presents an optimistic glimpse into novel treatments and interventions. As advancements in genetics and therapeutic strategies continue, the potential for improved quality of life for affected individuals grows.







